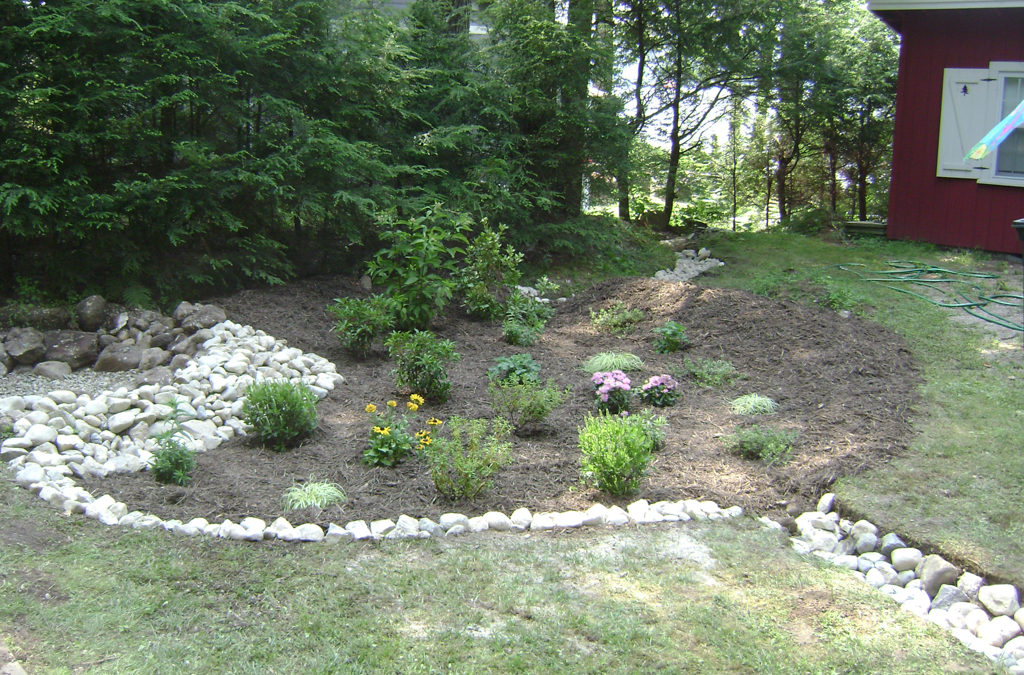
Rain Gardens
Managing roof runoff in your backyard
Purpose: Rain gardens are attractive and functional landscaped areas that are designed to capture and filter stormwater from roofs, driveways, and other hard surfaces. They collect water in bowl- shaped, vegetated areas, and allow it to slowly soak into the ground. This reduces the potential for erosion and minimizes the amount of pollutants flowing from your lawn into a storm drain, and eventually into our streams and lakes.
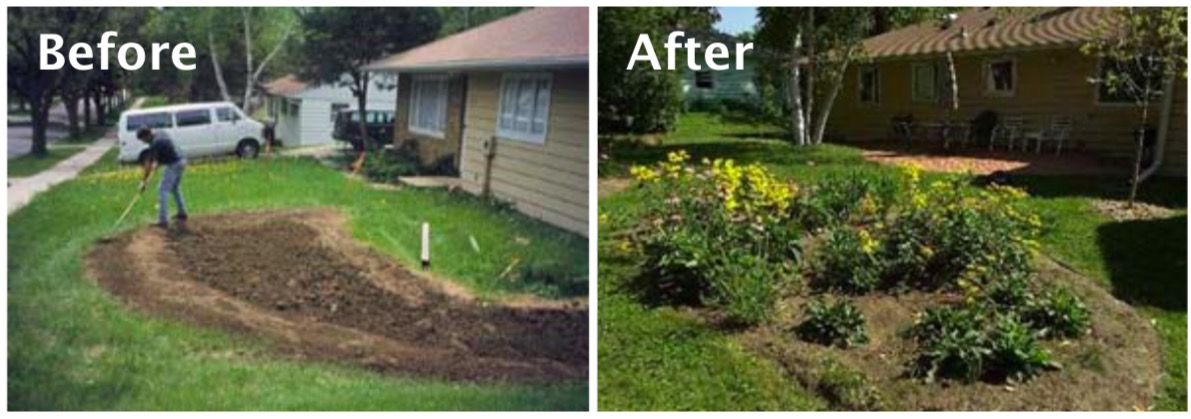
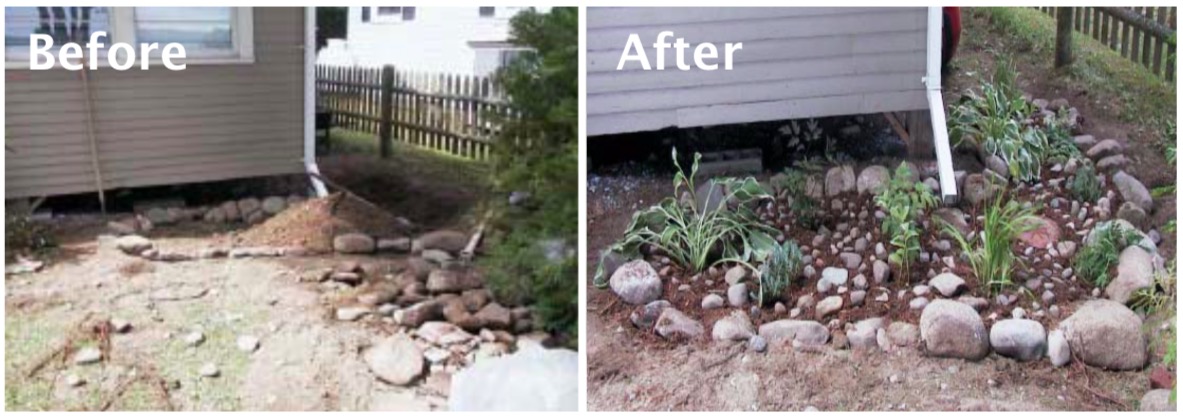


Installation:
Rain gardens can vary in size, but are most effective when built to 20-30% of the drainage area. Rain gardens for single-family homes will typically range from 150 to 300 square feet, but even a smaller one will help reduce water pollution problems.
- The garden should be bowl-shaped, with the lowest point of the garden no more than 6” below the surrounding land.
- The sides should be gently sloping towards the center to prevent sudden drop-offs that could lead to erosion problems or walking hazards.
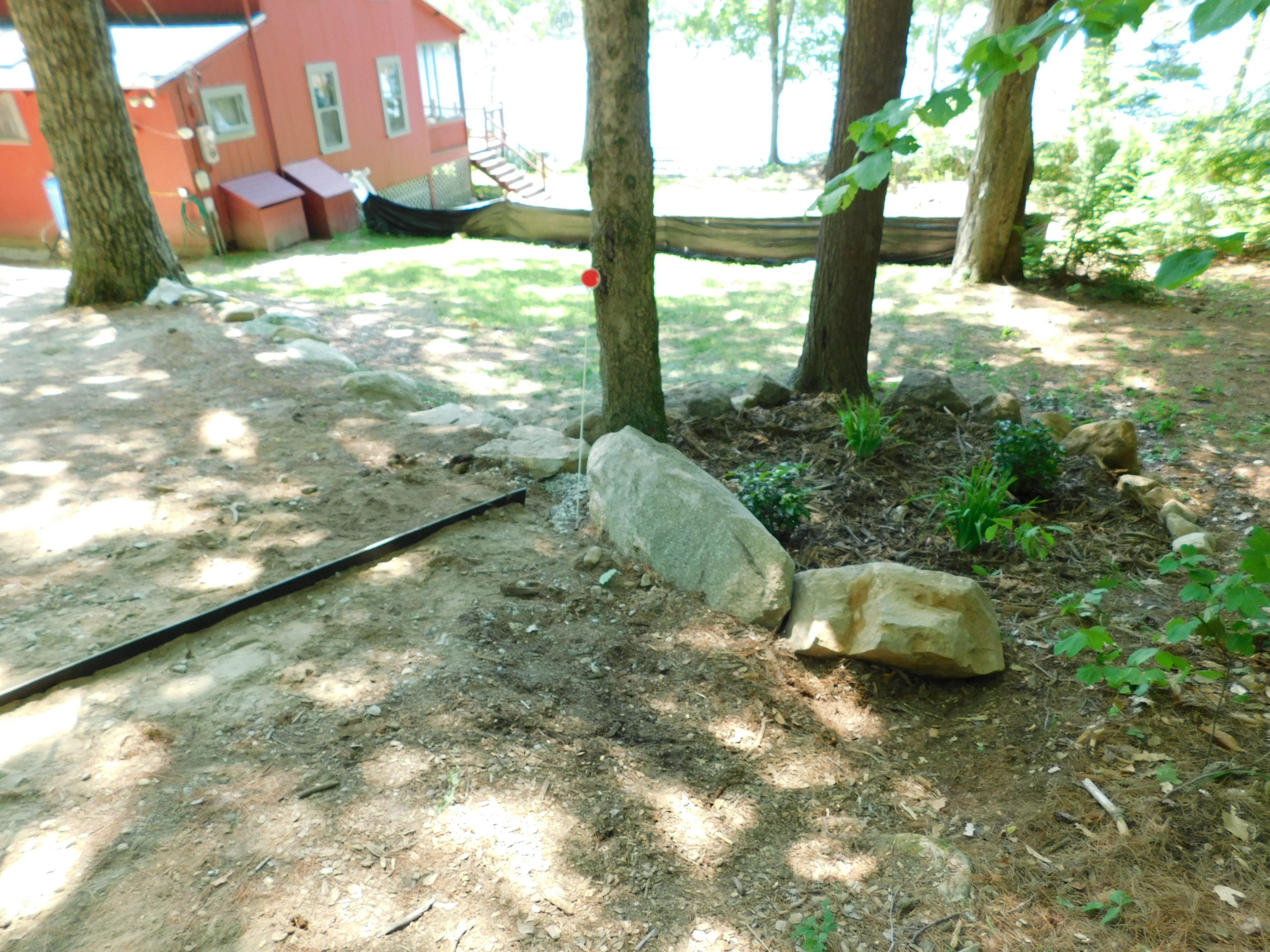
- Rain gardens are often placed in a preexisting or created depression within a lawn, or in a location that receives roof runoff from a downspout.
- To avoid flooding improperly sealed foundations, build your rain garden 10’ away from existing structures, and direct water into the garden with a grassy swale, French drain, gutter extension or other device.
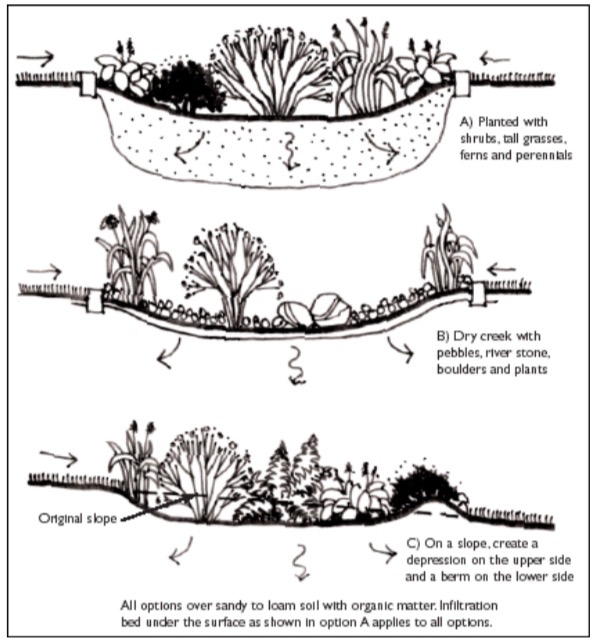
Rain gardens can be placed in sunny or shady regions of your lawn, but plants should be chosen accordingly, with the lowest point planted with wet tolerant species, the sides closest to the center planted with moist tolerant species, and the edges of the rain garden should be planted with sub- xeric (moist to dry) or xeric (dry) tolerant plants. It is also important to check the permeability of your soil.
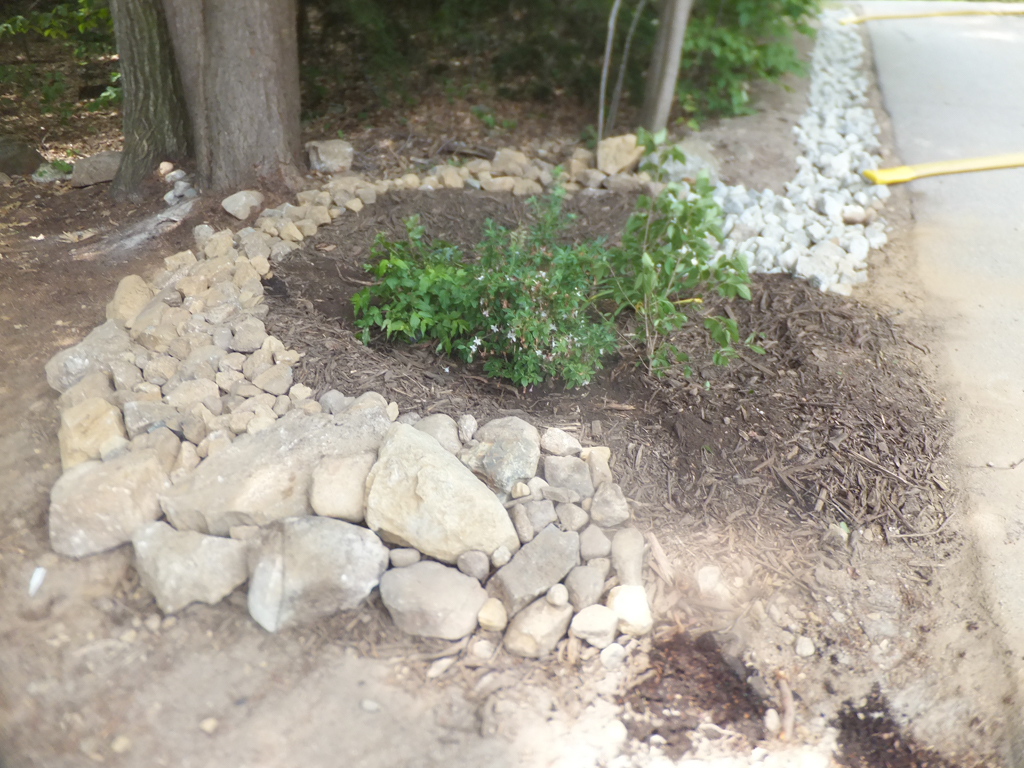

Sandy soils only need compost added, but clay soils should be replaced with a mix (50- 60% sand, 20-30% topsoil, 20-30% compost). After construction of the garden is complete, the entire area should be covered with a thick layer of mulch, preferably Erosion Control Mix.
Tip: Rain gardens can be added in conjunction with other BMPs. For example, these gardens can catch runoff coming from rubber razors (see photo below), and waterbars.

Materials: Replacement Soil mixes and Erosion Control Mix are available from local garden centers. Native plants can be purchased from your local nursery. Please see Native Plant Lists from this series for plant descriptions based on specific sun and soil conditions.
Maintenance: Overall, once plants mature, the maintenance of a rain garden is very low. Watering is important during the first growing season, and some weeding is necessary after planting. As the garden matures, some of the perennials may need to be divided if plantings become too crowded.
Examples
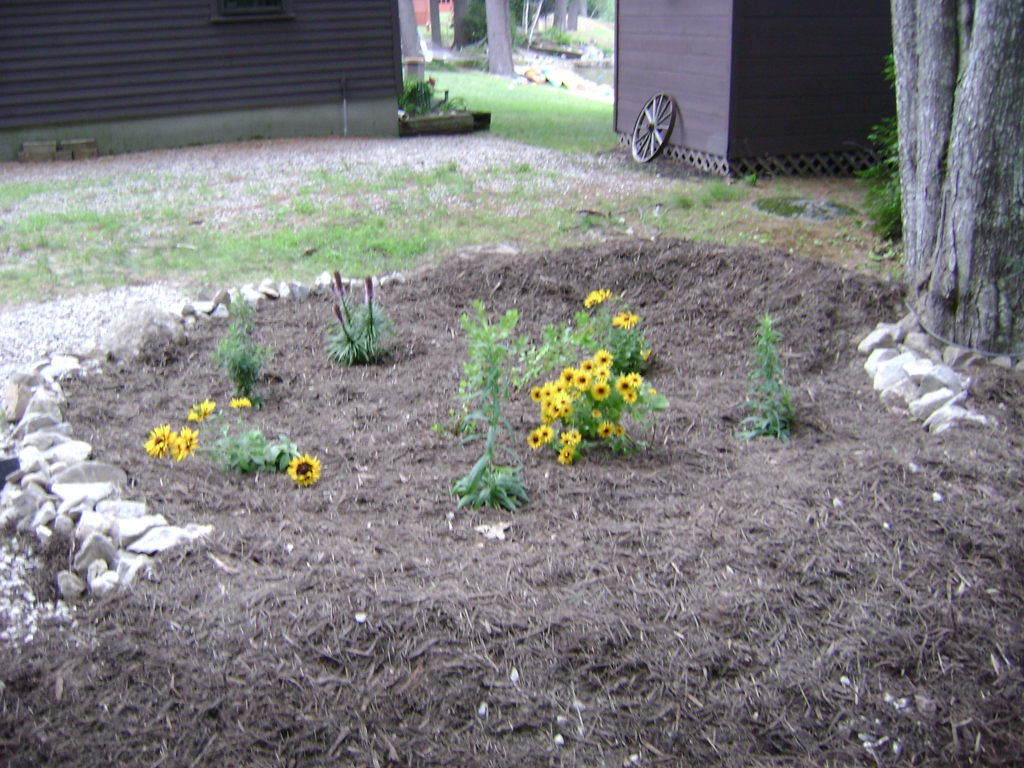
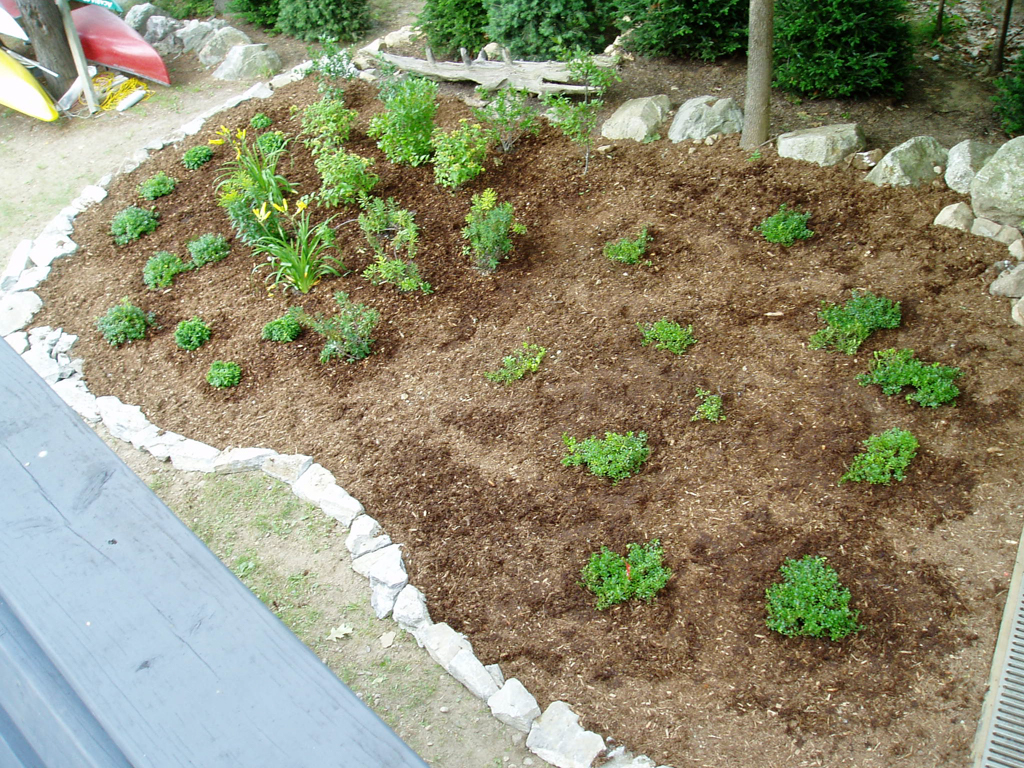
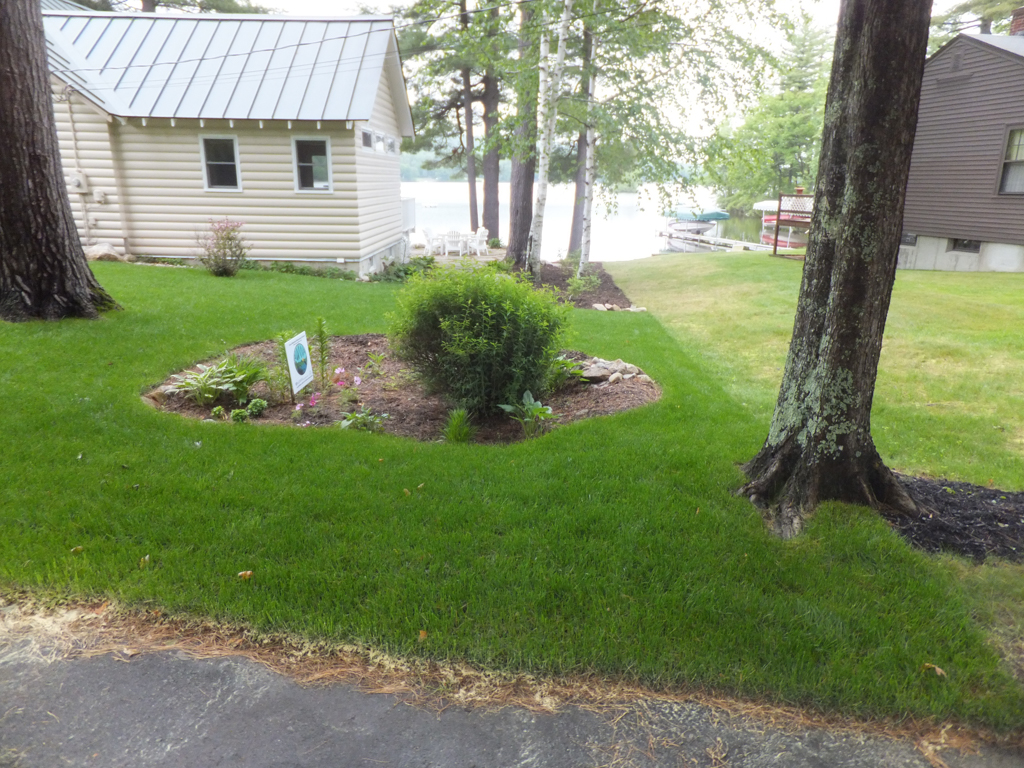
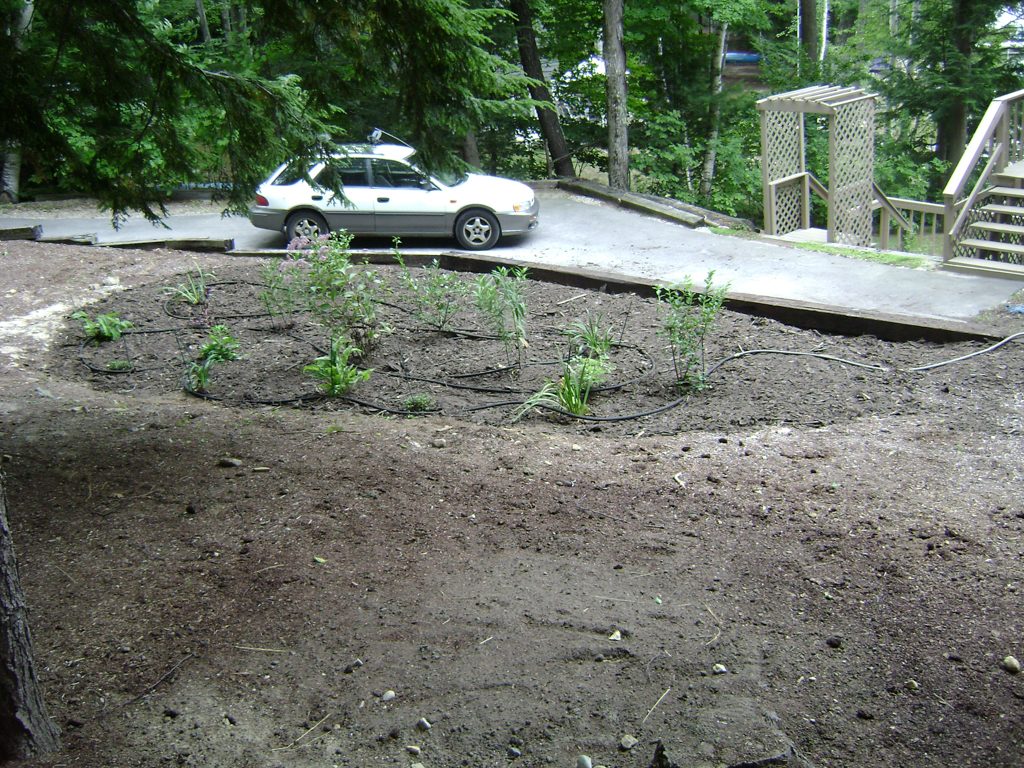
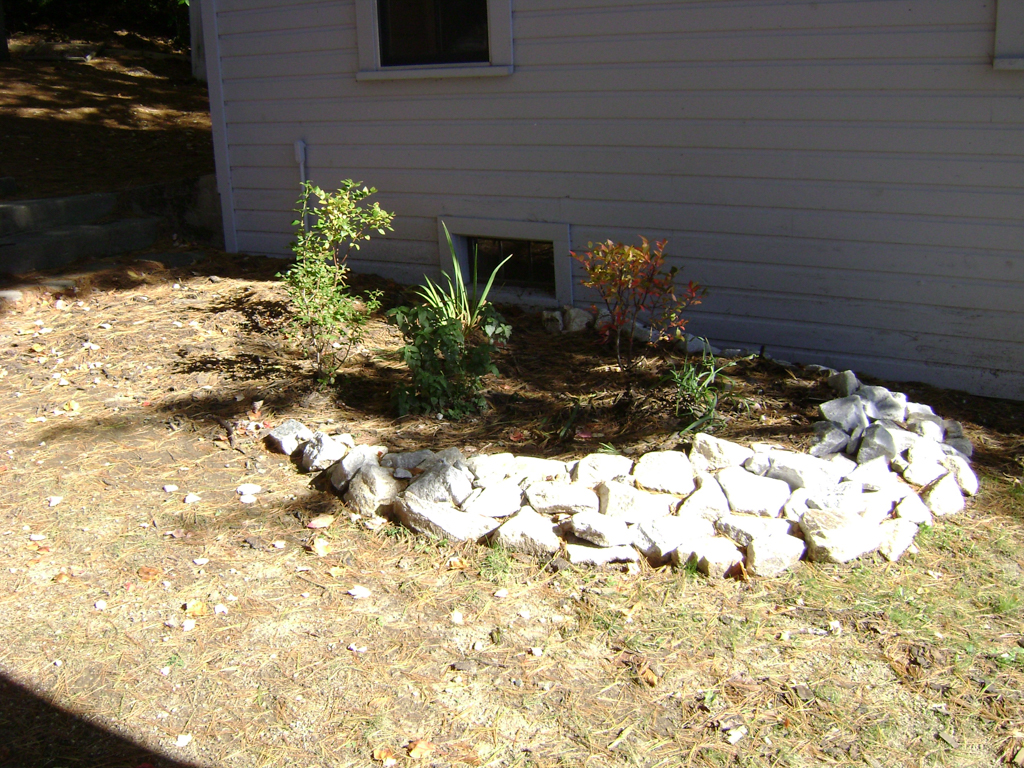
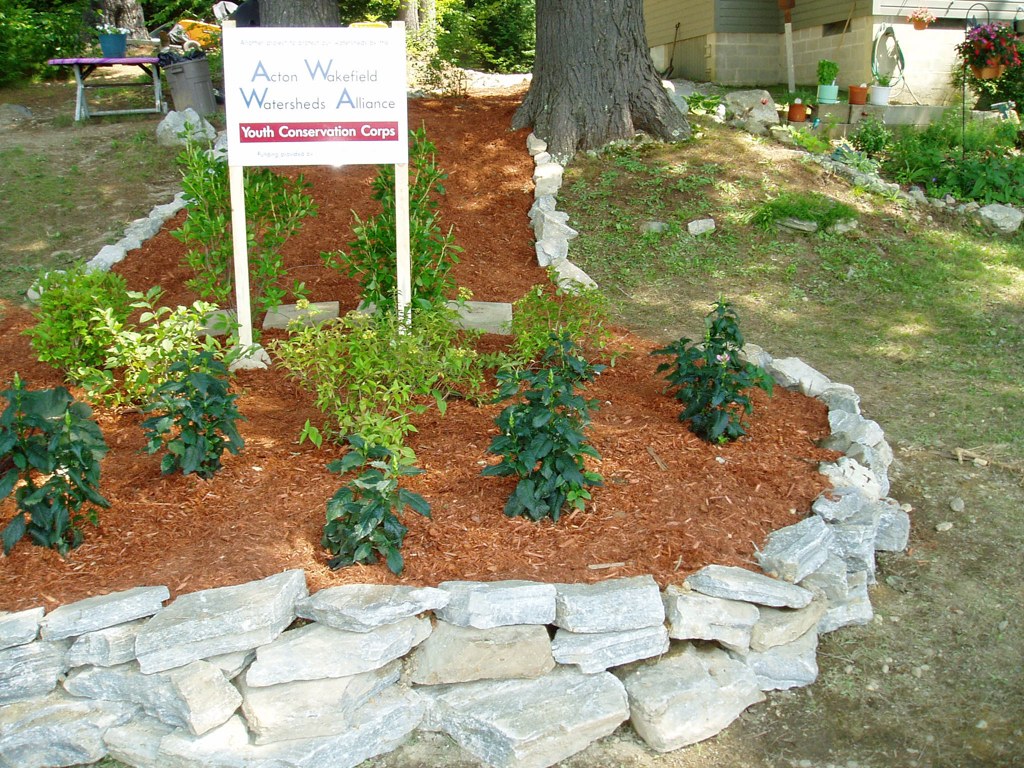
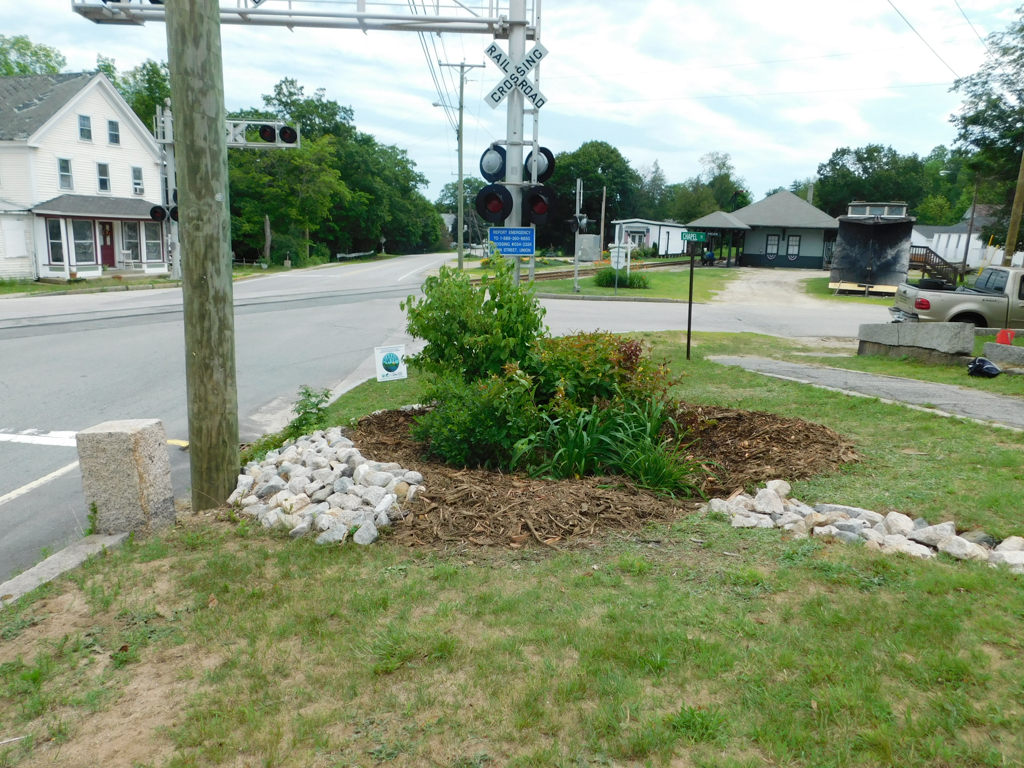







The Conservation Practices for Homeowners Factsheet Series are available at: Maine DEP or the Portland Water District. You can also find fact sheets at SOAK up the Rain NH.

